A03 | Quantification of Visual Explainability
High-dimensional data analysis requires dealing with numerous challenges, such as selecting meaningful dimensions, finding relevant projections, and removing noise. As a result, the extraction of relevant and meaningful information from high-dimensional data is a difficult problem. This project aims at advancing the field of quality-metric-driven data visualization with the central research question of how to quantify the quality of transformations and mappings of high-dimensional data for visual analytics.
Research Questions
How can we measure and quantify the quality of a visualization? In which way do methods in the data space differ from methods in the image space?
How can we compare the measured quality of a visualization with the perception of a human?
How can the user be involved into a quality-metric-driven process of visual mappings and transformations?
What is the influence of perceptual effects on quality measures? Can we enhance the visual representation of information by introducing perceptual effects into visualizations?
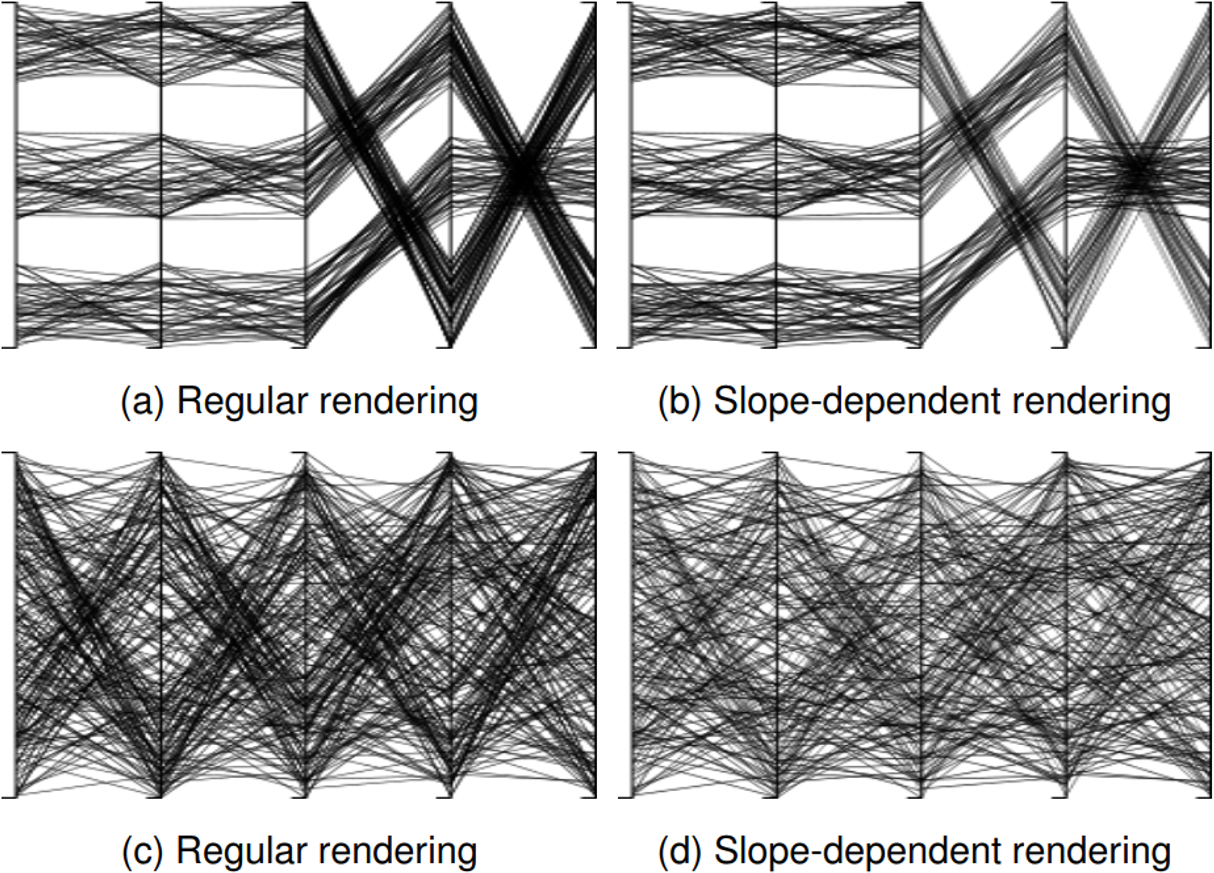
Fig. 1: Comparison of regular parallel coordinates with our slope-dependent polyline rendering. Parallel coordinates face two problems: Diagonal lines are rendered more closely (a), and zig-zag patterns are perceived as clusters, although there are no such clusters in the data (c). We render each line segment based on its slope between two axes. Cluster density is not distorted (b), and the zig-zag pattern effect is reduced (d).
Publications
- L. Joos, D. A. Keim, and M. T. Fischer, “Cutting Through the Clutter: The Potential of LLMs for Efficient Filtration in Systematic Literature Reviews,” in EuroVis Workshop on Visual Analytics (EuroVA), 2025. doi: 10.2312/eurova.20251105.
- L. Joos et al., “Show Me Your Best Side: Characteristics of User-Preferred Perspectives for 3D Graph Drawings,” in 33rd International Symposium on Graph Drawing and Network Visualization (GD 2025), 2025. doi: 10.4230/LIPIcs.GD.2025.35.
- R. Buchmüller, B. Jäckl, M. Behrisch, D. A. Keim, and F. L. Dennig, “cPro: Circular Projections Using Gradient Descent,” in Proceedings of the 15th International EuroVis Workshop on Visual Analytics (EuroVA), The Eurographics Association, 2024. doi: 10.2312/eurova.20241111.
- F. L. Dennig et al., “The Categorical Data Map: A Multidimensional Scaling-Based Approach,” in 2024 IEEE Visualization in Data Science (VDS), IEEE, 2024, pp. 25–34. doi: 10.1109/vds63897.2024.00008.
- L. Joos, B. Jäckl, D. A. Keim, M. T. Fischer, L. Peska, and J. Lokoč, “Known-Item Search in Video: An Eye Tracking-Based Study,” in Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval (ICMR ’24), New York, NY, USA: ACM, 2024, pp. 311–319. doi: 10.1145/3652583.3658119.
- D. Blumberg, Y. Wang, A. Telea, D. A. Keim, and F. L. Dennig, “Inverting Multidimensional Scaling Projections Using Data Point Multilateration,” in Proceedings of the 15th International EuroVis Workshop on Visual Analytics (EuroVA), The Eurographics Association, 2024. doi: 10.2312/eurova.20241112.
- L. Joos et al., “Evaluating Node Selection Techniques for Network Visualizations in Virtual Reality,” in ACM Symposium on Spatial User Interaction, New York, NY, USA: ACM, 2024, pp. 1–11. doi: 10.1145/3677386.3682102.
- J. Fuchs, F. L. Dennig, M.-V. Heinle, D. A. Keim, and S. Di Bartolomeo, “Exploring the Design Space of BioFabric Visualization for Multivariate Network Analysis,” Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 43, Art. no. 3, 2024, doi: 10.1111/cgf.15079.
- F. L. Dennig, M. Miller, D. A. Keim, and M. El-Assady, “FS/DS: A Theoretical Framework for the Dual Analysis of Feature Space and Data Space,” IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, pp. 1–17, 2023, [Online]. Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10158903
- Q. Q. Ngo, F. L. Dennig, D. A. Keim, and M. Sedlmair, “Machine Learning Meets Visualization – Experiences and Lessons Learned,” it - Information Technology, vol. 64, pp. 169–180, 2022, doi: 10.1515/itit-2022-0034.
- M. Kraus et al., “Immersive Analytics with Abstract 3D Visualizations: A Survey,” Computer Graphics Forum, 2021, doi: 10.1111/cgf.14430.
- M. Kraus, K. Klein, J. Fuchs, D. A. Keim, F. Schreiber, and M. Sedlmair, “The Value of Immersive Visualization,” IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications (CG&A), vol. 41, Art. no. 4, 2021, doi: 10.1109/MCG.2021.3075258.
- F. L. Dennig, M. T. Fischer, M. Blumenschein, J. Fuchs, D. A. Keim, and E. Dimara, “ParSetgnostics: Quality Metrics for Parallel Sets,” Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 40, Art. no. 3, 2021, doi: 10.1111/cgf.14314.
- M. Blumenschein, X. Zhang, D. Pomerenke, D. A. Keim, and J. Fuchs, “Evaluating Reordering Strategies for Cluster Identification in Parallel Coordinates,” Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 39, Art. no. 3, 2020, [Online]. Available: https://diglib.eg.org:443/handle/10.1111/cgf14000
- D. Schubring, M. Kraus, C. Stolz, N. Weiler, D. A. Keim, and H. Schupp, “Virtual Reality Potentiates Emotion and Task Effects of Alpha/Beta Brain Oscillations,” Brain Sciences, vol. 10, Art. no. 8, 2020, [Online]. Available: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3425/10/8/537
- L. Merino, M. Schwarzl, M. Kraus, M. Sedlmair, D. Schmalstieg, and D. Weiskopf, “Evaluating Mixed and Augmented Reality: A Systematic Literature Review (2009 – 2019),” in IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR), 2020. [Online]. Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9284762
- M. Blumenschein, L. J. Debbeler, N. C. Lages, B. Renner, D. A. Keim, and M. El-Assady, “v-plots: Designing Hybrid Charts for the Comparative Analysis of Data Distributions,” Computer Graphics Forum, vol. 39, Art. no. 3, 2020, doi: 10.1111/cgf14002.
- M. Kraus et al., “Assessing 2D and 3D Heatmaps for Comparative Analysis: An Empirical Study,” in Proceedings of the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, 2020, pp. 546:1–546:14. doi: 10.1145/3313831.3376675.
- D. R. Wahl et al., “Why We Eat What We Eat: Assessing Dispositional and In-the-Moment Eating Motives by Using Ecological Momentary Assessment,” JMIR mHealth and uHealth., vol. 8, Art. no. 1, 2020, [Online]. Available: https://mhealth.jmir.org/2020/1/e13191/
- M. Blumenschein, “Pattern-Driven Design of Visualizations for High-Dimensional Data,” Konstanz, 2020. [Online]. Available: http://nbn-resolving.de/urn:nbn:de:bsz:352-2-18wp9dhmhapww8
- M. Kraus et al., “A Comparative Study of Orientation Support Tools in Virtual Reality Environments with Virtual Teleportation,” in 2020 IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality (ISMAR), 2020, pp. 227–238. [Online]. Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9284697
- C. Schätzle, F. L. Dennig, M. Blumenschein, D. A. Keim, and M. Butt, “Visualizing Linguistic Change as Dimension Interactions,” in Proceedings of the International Workshop on Computational Approaches to Historical Language Change, 2019, pp. 272–278. [Online]. Available: https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/W19-4734.pdf
- D. Pomerenke, F. L. Dennig, D. A. Keim, J. Fuchs, and M. Blumenschein, “Slope-Dependent Rendering of Parallel Coordinates to Reduce Density Distortion and Ghost Clusters,” in Proceedings of the IEEE Visualization Conference (VIS), IEEE, 2019, pp. 86–90. [Online]. Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8933706
- M. Miller, X. Zhang, J. Fuchs, and M. Blumenschein, “Evaluating Ordering Strategies of Star Glyph Axes,” in Proceedings of the IEEE Visualization Conference (VIS), IEEE, 2019, pp. 91–95. [Online]. Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8933656
- F. L. Dennig, T. Polk, Z. Lin, T. Schreck, H. Pfister, and M. Behrisch, “FDive: Learning Relevance Models using Pattern-based Similarity Measures,” Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Visual Analytics Science and Technology (VAST), 2019, [Online]. Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8986940
- M. Blumenschein et al., “SMARTexplore: Simplifying High-Dimensional Data Analysis through a Table-Based Visual Analytics Approach,” in Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Visual Analytics Science and Technology (VAST), R. Chang, H. Qu, and T. Schreck, Eds., IEEE, 2018, pp. 36–47. [Online]. Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8802486
- L. J. Debbeler, M. Gamp, M. Blumenschein, D. A. Keim, and B. Renner, “Polarized But Illusory Beliefs About Tap and Bottled Water: A Product- and Consumer-Oriented Survey and Blind Tasting Experiment,” Science of the Total Environment, vol. 643, pp. 1400–1410, 2018, doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.190.
- D. Sacha et al., “SOMFlow: Guided Exploratory Cluster Analysis with Self-Organizing Maps and Analytic Provenance,” IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, vol. 24, Art. no. 1, 2018, [Online]. Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8019867
- M. Behrisch et al., “Magnostics: Image-Based Search of Interesting Matrix Views for Guided Network Exploration,” IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, vol. 23, Art. no. 1, 2017, [Online]. Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7534849
- M. Stein et al., “Bring it to the Pitch: Combining Video and Movement Data to Enhance Team Sport Analysis,” in IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2017, pp. 13–22. [Online]. Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8019849
- D. Jäckle, F. Stoffel, S. Mittelstädt, D. A. Keim, and H. Reiterer, “Interpretation of Dimensionally-Reduced Crime Data: A Study with Untrained Domain Experts,” in Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision, Imaging and Computer Graphics Theory and Applications (VISIGRAPP), 2017, pp. 164–175. [Online]. Available: https://bib.dbvis.de/publications/details/697
- D. Jäckle, M. Hund, M. Behrisch, D. A. Keim, and T. Schreck, “Pattern Trails: Visual Analysis of Pattern Transitions in Subspaces,” in Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Visual Analytics Science and Technology (VAST), B. Fisher, S. Liu, and T. Schreck, Eds., IEEE, 2017, pp. 1–12. [Online]. Available: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8585613
- M. Hund et al., “Visual Analytics for Concept Exploration in Subspaces of Patient Groups,” Brain Informatics, vol. 3, Art. no. 4, 2016, doi: 10.1007/s40708-016-0043-5.
- M. Hund et al., “Visual Quality Assessment of Subspace Clusterings,” in Proceedings of the KDD Workshop on Interactive Data Exploration and Analytics (IDEA), I. KDD 2016, Ed., 2016, pp. 53–62.
- C. Schulz et al., “Generative Data Models for Validation and Evaluation of Visualization Techniques,” in Proceedings of the Workshop on Beyond Time and Errors: Novel Evaluation Methods for Visualization (BELIV), ACM, 2016, pp. 112–124. doi: 10.1145/2993901.2993907.
- M. Hund et al., “Subspace Nearest Neighbor Search - Problem Statement, Approaches, and Discussion,” in Similarity Search and Applications. International Conference on Similarity Search and Applications (SISAP). Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 9371, G. Amato, R. Connor, F. Falchi, and C. Gennaro, Eds., in Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 9371. , Springer, Cham, 2015, pp. 307–313. [Online]. Available: https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007%2F978-3-319-25087-8_29
FOR SCIENTISTS
Projects
People
Publications
Graduate School
Equal Opportunity
FOR PUPILS
PRESS AND MEDIA
© SFB-TRR 161 | Quantitative Methods for Visual Computing | 2019.