C03 | Immersive Virtual Environments
Nina Flad, Max Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics
Menja Scheer, Max Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics
Alessandro Nesti, Max Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics
Christiane Glatz, Max Planck Institute for Biological Cybernetics
Immersive virtual environments (IVEs) simulate real-world scenarios for purposes ranging from entertainment to safety-critical training (e.g., surgery, driving or flying). This project investigates how computationally demanding IVEs can be optimized to ensure realistic user performance, by focusing on how users seek out and process information for real-time operations. For this purpose, mobile gaze-tracking and EEG methods will be extended for use in IVEs. The context for research is aircraft simulation because it encompasses the rendering demands of a realistic world scene, intuitive visualization of in-vehicle instrumentation, and accurate synchronization of non-visual modalities (i.e., real motion).
Research Questions
How can users in IVEs be unobtrusively monitored without interrupting their activity?
How should visual information seeking and processing behavior be interpreted for the evaluation of visual computing?
How should visualizations be effectively combined with non-visual cues in a moving base simulator?
How are visualizations in IVE simulators relied on to support complex closed-loop control behavior?
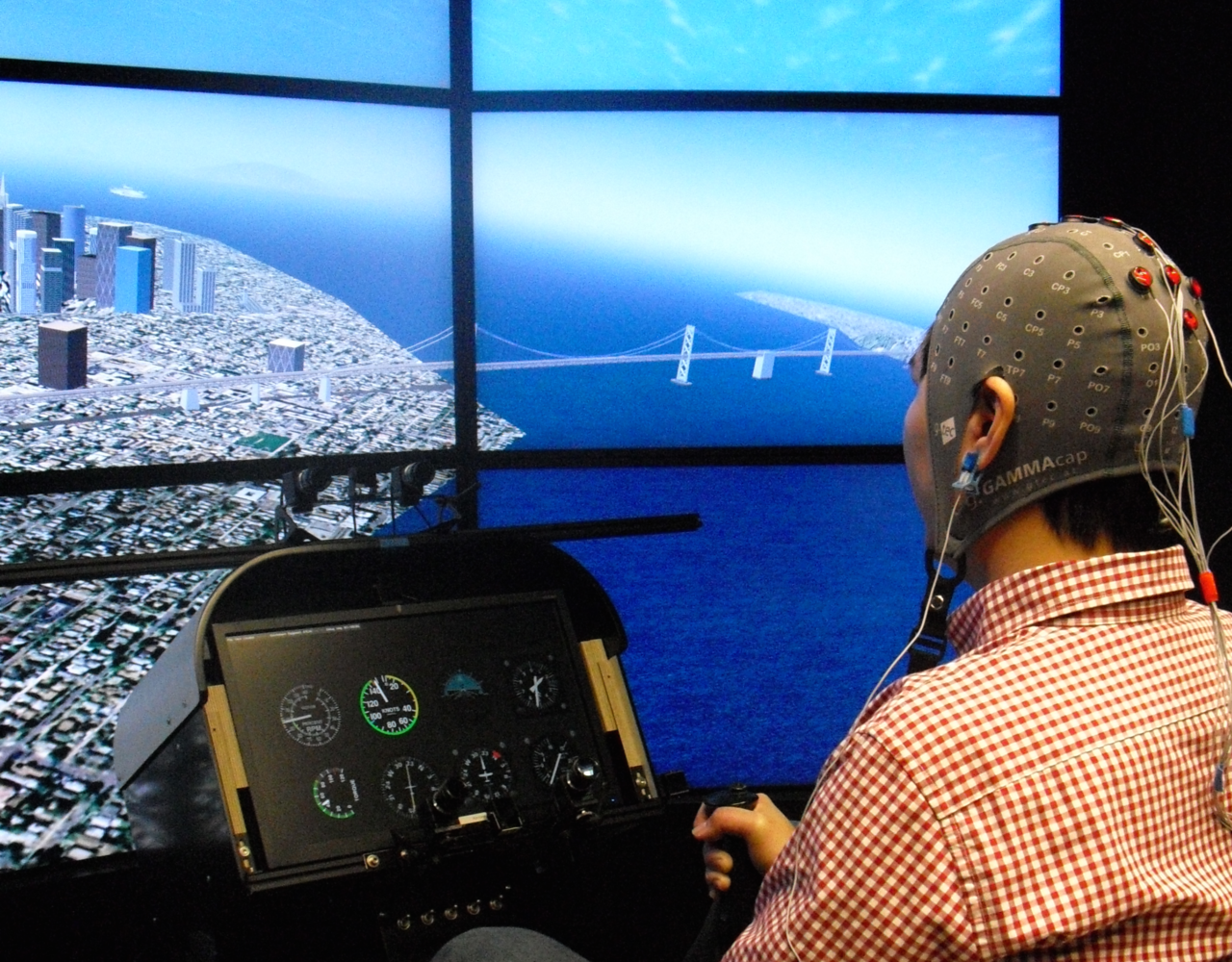
Fig. 1: Immersive virtual environments provide visualisations in the form of a realistic world environment as well as abstract instruments. Both are important in supporting user interaction, especially in vehicle handling simulators (e.g., flight simulator). Gaze-tracking and electrophysiological recordings (e.g., EEG/ERP, heart-based measures) are respectively employed to evaluate how visual information is sought out and processed.
Publications
FOR SCIENTISTS
Projects
People
Publications
Graduate School
Equal Opportunity
FOR PUPILS
PRESS AND MEDIA
© SFB-TRR 161 | Quantitative Methods for Visual Computing | 2019.